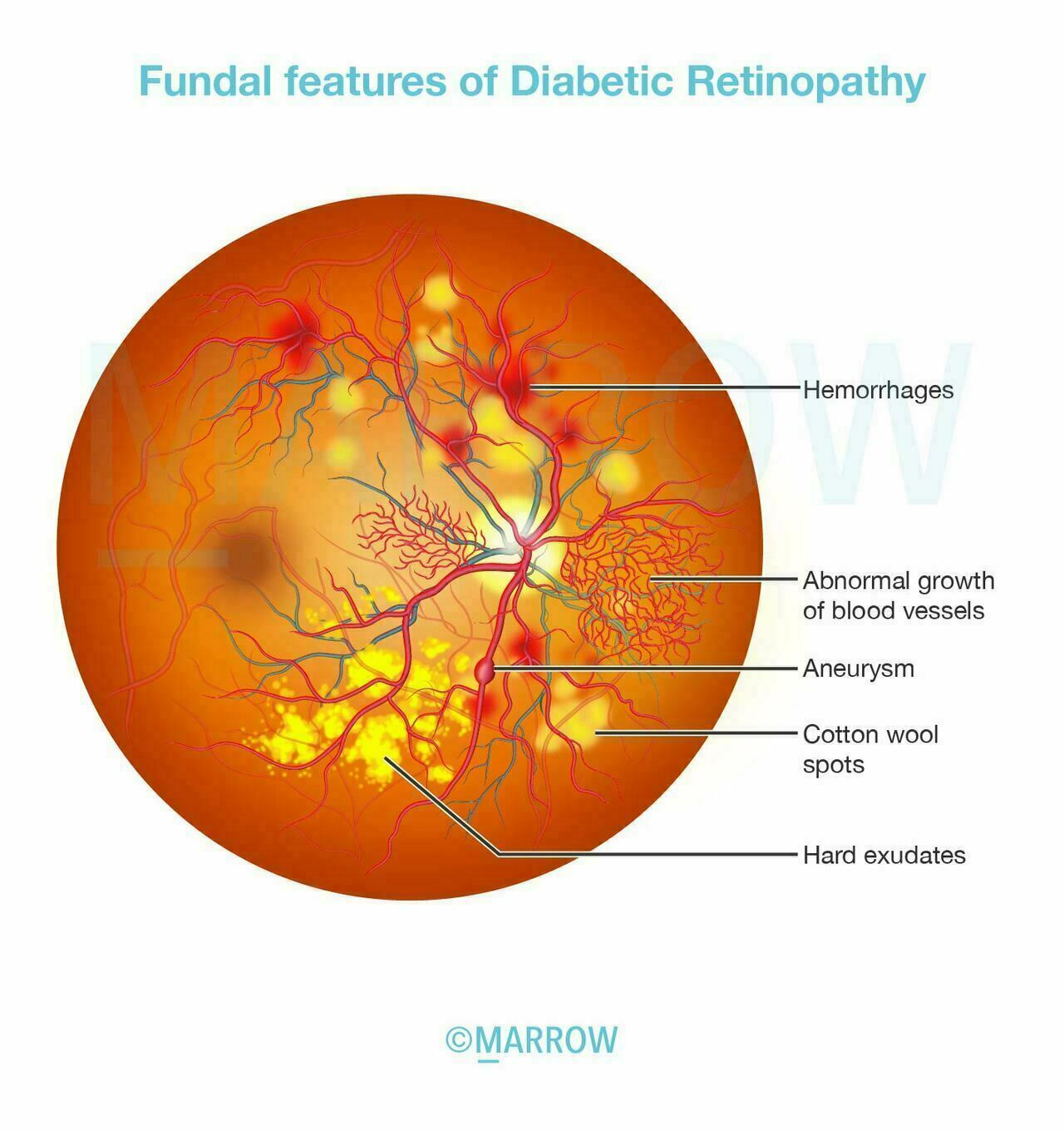
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR):
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR):
Clinically significant macular edema: 1 of the following 3 criteria are present on slit-lamp examination with 90D lens
Advanced diabetic eye disease:
- Mild NPDR
- At least one microaneurysm must be present
- Moderate NPDR
- Microaneurysms/intraretinal hemorrhage in 2 or 3 quadrants
- Early mild intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA)
- Hard exudates and cotton-wool spots may or may not be present
- Severe NPDR - any one of the following (4-2-1 rule)
- 4 quadrants of microaneurysms and extensive intraretinal hemorrhages
- 2 quadrants of venous beading
- 1 quadrant of IRMA changes
- Very severe NPDR - any two of the following (4-2-1)
- 4 quadrants of microaneurysms and extensive intraretinal hemorrhages
- 2 quadrants of venous beading
- 1 quadrant of IRMA changes
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR):
- PDR without high-risk characteristics (Early PDR)
- Early neovascularization at the optic disc (NVD) or neovascularization elsewhere (NVE)
- PDR with high-risk characteristics as follows
- NVD < 1/4 disc area with vitreous hemorrhage (VH) or preretinal hemorrhage (PRH)
- NVD 1/4 to 1/3 of disc area with or without VH or PRH
- NVE > 1/2 disc area with VH or PRH
Clinically significant macular edema: 1 of the following 3 criteria are present on slit-lamp examination with 90D lens
- Thickening of the retina at or within 500 micron of the center of the fovea.
- Hard exudates at or within 500 micron of the centre of fovea associated with adjacent retinal thickening.
- Development of a zone of retinal thickening one disc diameter or larger in size. At least a part of this should be within one disc diameter of the foveal center.
Advanced diabetic eye disease:
- Persistent vitreous hemorrhage
- Tractional retinal detachment
- Neovascular glaucoma