Tuberous sclerosis (TS) is also known as tuberous sclerosis complex or Bourneville disease. It is a neurocutaneous disorder (phakomatosis) characterized by the development of multiple benign tumors of the embryonic ectoderm (e.g. skin, eyes, and nervous system). It is an autosomal dominant condition. The mutations are involved in the TSC1 gene that encodes hamartin on chromosome 9 and the TSC2 gene that encodes a protein tuberin on chromosome 16.
Tuberous sclerosis presents in childhood with a triad (Vogt triad). The triad comprises of:
Skin lesions in tuberous sclerosis:
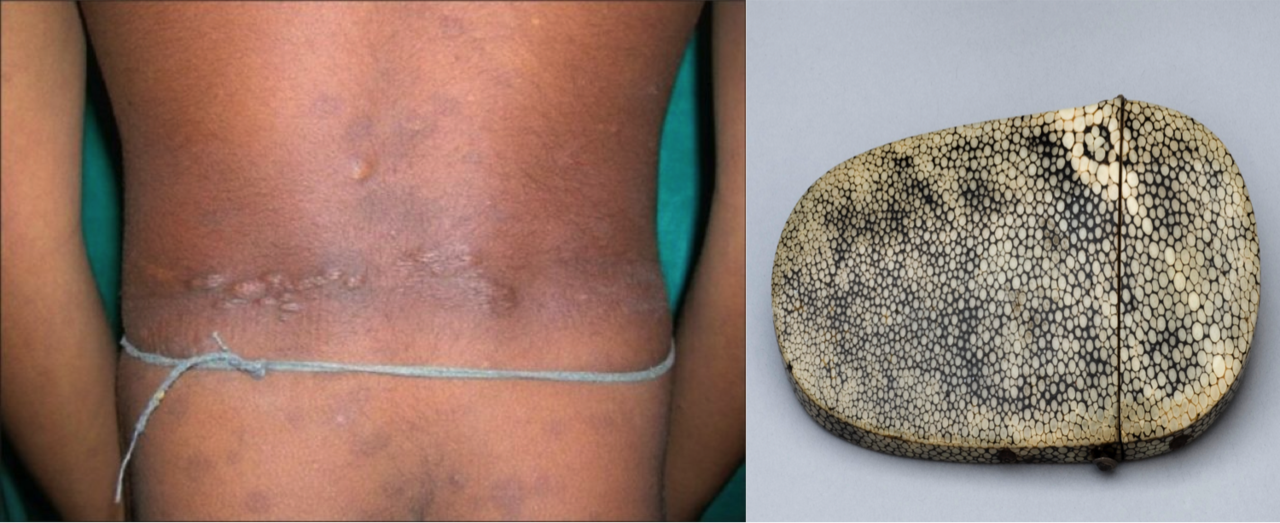
Shagreen patch consists of a roughened, raised lesion with an orange-peel consistency, located primarily in the lumbosacral region. Shagreen is shark skin used as a decorative material present in the right image given below.
Tuberous sclerosis presents in childhood with a triad (Vogt triad). The triad comprises of:
- Seizures
- Mental retardation
- Adenoma sebaceum
Skin lesions in tuberous sclerosis:
Shagreen patch consists of a roughened, raised lesion with an orange-peel consistency, located primarily in the lumbosacral region. Shagreen is shark skin used as a decorative material present in the right image given below.
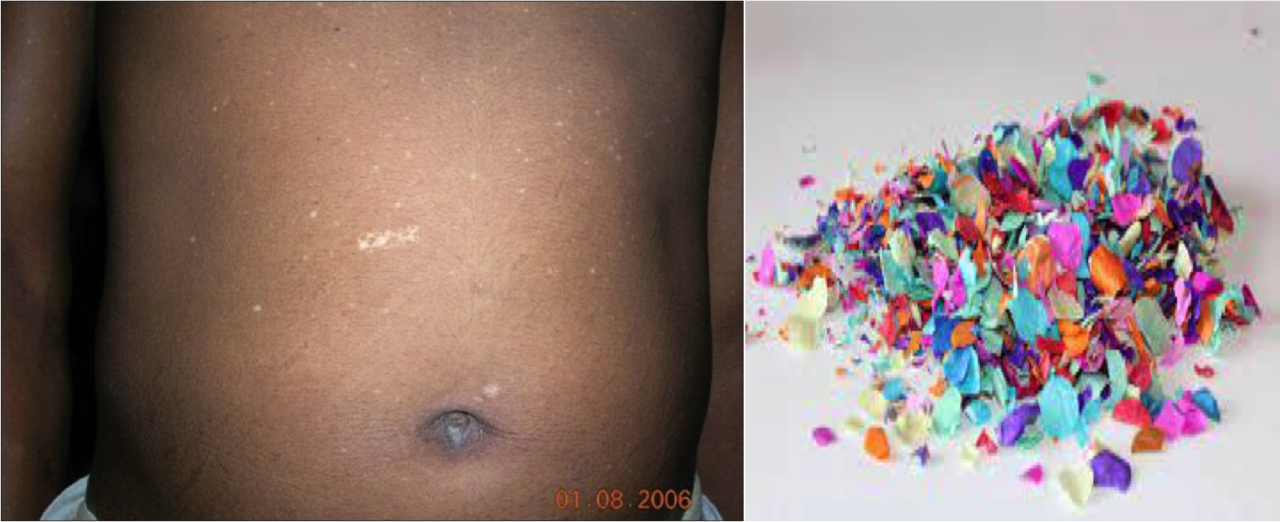
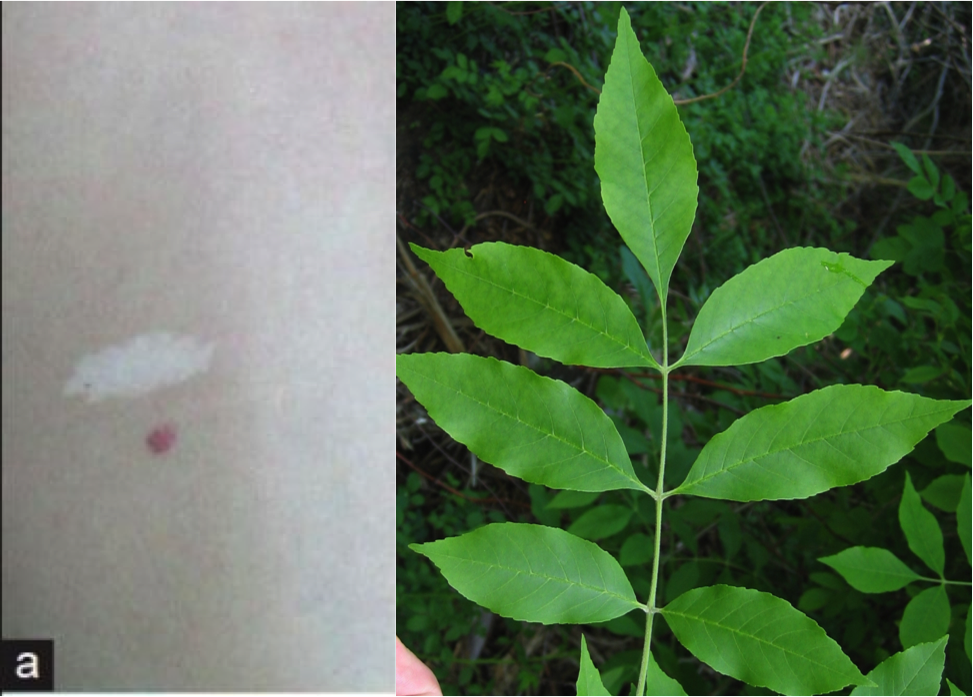
The typical hypomelanotic ash leaf–type macules on the trunk and extremities are seen in 90% of the patients. It is visualized by the use of a wood ultraviolet lamp.

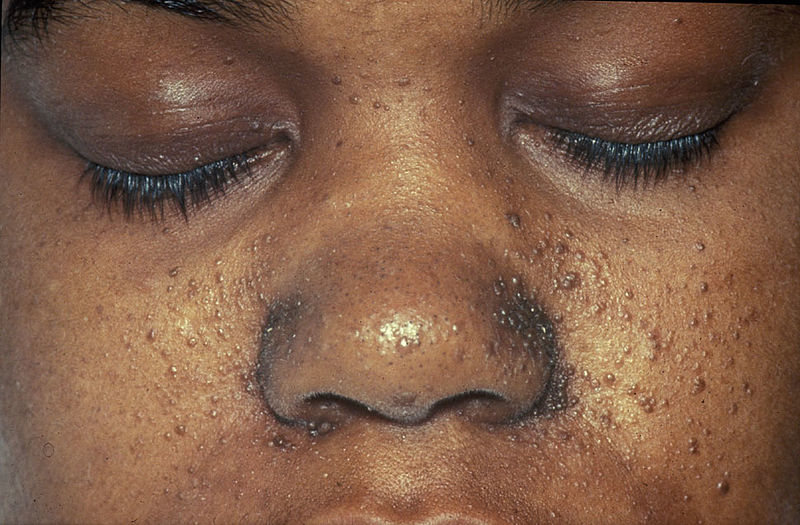
Facial angiofibromas (adenoma sebaceum) develop between 4 and 6 years of age; they appear as tiny red nodules over the nose and cheeks and are sometimes confused with acne. Later, they enlarge, coalesce, and assume a fleshy appearance.
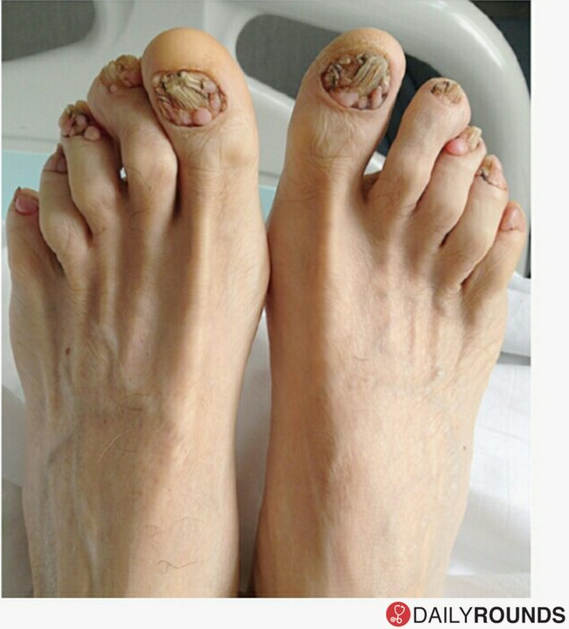
Periungual fibroma are small fibromas or nodules of skin, which form around fingernails or toenails in some adolescent patients
Confetti skin lesions are seen less commonly as a minor feature of tuberous sclerosis.